Introduction
When organizations think about integrating AI assistants into their applications, they often picture a chatbot widget floating in the corner of the screen. But what if you could harness the power of Microsoft Copilot Studio Agents while keeping your existing user interface exactly as it is?
Enter the Direct Line API — a powerful yet underutilized approach that allows any custom application to communicate with Copilot Studio Agents programmatically. This opens up a world of possibilities for embedding intelligent automation into your applications without compromising on user experience.
In this blog, we’ll explore how this integration works and dive into practical use cases across various industries.
What is the Direct Line API?
The Direct Line API is part of the Microsoft Bot Framework that enables direct communication between your application and a bot (or in this case, a Copilot Studio Agent) via REST APIs. Unlike traditional chatbot integrations that require embedding a chat widget, Direct Line allows you to:
- Send events to trigger specific agent topics
- Receive structured responses from the agent
- Maintain complete control over your application’s UI/UX
Think of it as a backend integration your users interact with your familiar interface, while the AI processing happens seamlessly behind the scenes.
The Architecture
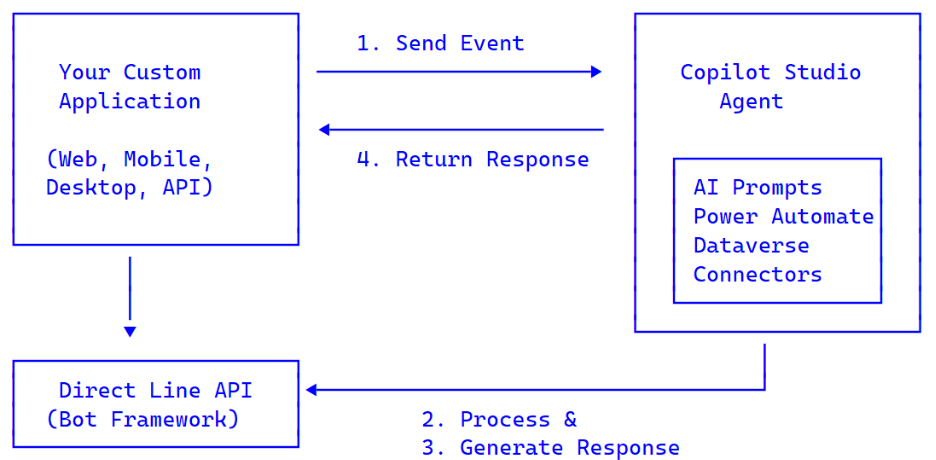
Integration Flow
- Authenticate — Get a token from the Power Platform token endpoint.
- Start Conversation — Initialize a Direct Line conversation.
- Send Event — Trigger a specific Copilot Studio topic with your payload.
- Poll for Response — Receive the AI-processed result.
- Update UI — Display the results in your application.
Why This Pattern is Powerful
| Benefit | Description |
| Custom UX | Keep your app’s look and feel — no chatbot widget needed |
| Event-Driven | Trigger specific topics for specific actions (not generic chat) |
| Power Platform | Access Dataverse, Power Automate flows, 1000+ connectors |
| Centralized AI | Manage prompts and logic in Copilot Studio without code deployments |
| Audit & Analytics | Built-in conversation analytics and monitoring |
| Multi-channel | Same agent can serve web, Teams, mobile, and more |
| Security | Leverage Power Platform security, DLP policies, and governance |
| Scalability | Serverless scaling handled by Microsoft infrastructure |
Real-World Use Cases
Let’s explore how this pattern can be applied across different industries and scenarios.
1. Document Processing & Content Refinement
Pattern: Document App → Agent → Refine & enhance content
Scenario: A document authoring application needs AI-powered content enhancement.
How it works:
– User writes content in your application
– Application sends content to Copilot Studio Agent via event
– Agent refines, summarizes, or reformats the content
– Polished content returns to the application
Example Event:
{
“name”: “RefineContentEvent”,
“value”: {
“text”: “Raw content from user…”,
“instructions”: “Make it more professional and concise”
}
}
Use Cases:
– Technical documentation tools
– Email composition assistants
– Report generators
– Marketing copy enhancement
2. Customer Support Automation
Pattern: Support Portal → Agent → Categorize & suggest resolutions
Scenario: A support portal needs intelligent ticket triage and resolution suggestions.
How it works:
– Customer submits issue description
– Agent analyzes and categorizes the ticket
– Returns category, priority, and suggested KB articles
– Support team sees enriched ticket data
Example Event:
{
“name”: “TriageTicketEvent”,
“value”: {
“description”: “Cannot access email on mobile device”,
“customerTier”: “Premium”,
“productArea”: “Mobile App”
}
}
Outputs:
– Ticket category and subcategory
– Priority level (with justification)
– Relevant knowledge base articles
– Suggested resolution steps
– Escalation recommendation
3. HR Self-Service Applications
Pattern: Employee Portal → Agent → Policy lookup & request processing
Scenario: An employee portal needs intelligent policy assistance and request processing.
How it works:
– Employee asks a policy question or submits a request
– Agent queries HR knowledge base or validates against policies
– Returns accurate information or processes the request
– Can trigger Power Automate flows for approvals
Example Event:
{
“name”: “PolicyInquiryEvent”,
“value”: {
“question”: “What is the parental leave policy for new fathers?”,
“employeeLocation”: “California”,
“employeeType”: “Full-time”
}
}
Use Cases:
– Benefits inquiries
– Leave request validation
– Onboarding task assistance
– Policy clarification
4. Sales Enablement Tools
Pattern: Sales Dashboard → Agent → Lead scoring & content generation
Scenario: A sales dashboard needs AI-powered lead scoring and content generation.
How it works:
– Sales rep views a lead profile
– Application sends lead data to agent
– Agent analyzes fit and returns score with recommendations
– Can also generate personalized outreach content
Example Event:
{
“name”: “ScoreLeadEvent”,
“value”: {
“company”: “Acme Corporation”,
“industry”: “Manufacturing”,
“companySize”: 500,
“engagementHistory”: [“Whitepaper download”, “Webinar attended”, “Pricing page visit”]
}
}
Outputs:
– Lead score (1-100)
– Fit analysis
– Recommended next actions
– Personalized talking points
– Competitive positioning notes
5. IT Service Desk Integration
Pattern: IT Portal → Agent → Smart triage & self-service resolution
Scenario: An IT portal needs smart ticket routing and self-service resolution.
How it works:
– User describes their IT issue
– Agent categorizes and checks for self-service options
– Returns resolution steps or creates a properly routed ticket
– Can trigger automated remediation via Power Automate
Example Event:
{
“name”: “ITSupportEvent”,
“value”: {
“issueDescription”: “Outlook keeps crashing when I open attachments”,
“deviceType”: “Windows Laptop”,
“urgency”: “Medium”
}
}
Outputs:
– Issue category (Email, Hardware, Network, etc.)
– Self-service resolution steps
– Ticket creation (if needed)
– Estimated resolution time
– Workaround suggestions
6. Field Service Applications
Pattern: Technician App → Agent → Troubleshooting & parts lookup
Scenario: A technician’s mobile app needs real-time troubleshooting assistance.
How it works:
– Technician enters error code or describes issue
– Agent queries service manuals and historical data
– Returns step-by-step troubleshooting guide
– Can identify required parts and check inventory
Example Event:
{
“name”: “TroubleshootEvent”,
“value”: {
“equipmentModel”: “HVAC-3000X”,
“errorCode”: “E45”,
“symptoms”: “Unit not cooling, fan running normally”
}
}
Outputs:
– Diagnosis summary
– Step-by-step repair instructions
– Required parts list
– Safety warnings
– Historical fix success rates
7. Educational Platforms
Pattern: LMS → Agent → Tutoring & assessment generation
Scenario: A learning management system needs AI-powered tutoring and assessment.
How it works:
– Student asks a question or requests practice problems
– Agent generates tailored explanations or assessments
– Returns content appropriate to the student’s level
– Can track learning progress via Dataverse
Example Event:
{
“name”: “GenerateQuizEvent”,
“value”: {
“topic”: “Quadratic Equations”,
“difficulty”: “Intermediate”,
“questionCount”: 5,
“studentGradeLevel”: 10
}
}
Outputs:
– Generated quiz questions
– Answer key with explanations
– Hints for struggling students
– Related topics for further study
8. Financial Services Applications
Pattern: Banking App → Agent → Analysis & financial guidance
Scenario: A banking app needs intelligent transaction analysis and financial guidance.
How it works:
– Application sends transaction data or financial query
– Agent analyzes patterns or calculates eligibility
– Returns insights, recommendations, or qualification status
– All within compliance guardrails
Example Event:
{
“name”: “SpendingAnalysisEvent”,
“value”: {
“timeframe”: “Last 3 months”,
“categories”: [“Dining”, “Entertainment”, “Shopping”],
“accountType”: “Checking”
}
}
Outputs:
– Spending breakdown by category
– Trend analysis
– Savings opportunities
– Budget recommendations
– Comparison to similar profiles
9. Healthcare Patient Portals
Pattern: Patient Portal → Agent → Appointment prep & health guidance
Scenario: A patient app needs intelligent appointment preparation and health guidance.
How it works:
– Patient has an upcoming appointment or health question
– Agent provides preparation instructions or validated information
– Returns personalized guidance with appropriate disclaimers
– Maintains HIPAA compliance throughout
Example Event:
{
“name”: “AppointmentPrepEvent”,
“value”: {
“appointmentType”: “Annual Physical”,
“patientAge”: 45,
“existingConditions”: [“Hypertension”]
}
}
Outputs:
– Pre-appointment checklist
– Required fasting instructions
– Documents to bring
– Questions to ask the doctor
– Health metrics to track beforehand
10. Legal and Compliance Tools
Pattern: Contract System → Agent → Clause analysis & risk assessment
Scenario: A contract management system needs intelligent clause analysis.
How it works:
– User submits contract clause for review
– Agent analyzes against company policies and standards
– Returns compliance status and suggested modifications
– Can flag risks for legal team review
Example Event:
{
“name”: “ClauseReviewEvent”,
“value”: {
“clauseText”: “Limitation of liability shall not exceed the total fees paid…”,
“contractType”: “SaaS Agreement”,
“contractValue”: 500000,
“jurisdiction”: “Delaware”
}
}
Outputs:
– Compliance status (Approved/Needs Review/Rejected)
– Risk assessment
– Suggested alternative language
– Relevant policy references
– Similar approved clauses
Implementation Guide
Prerequisites
- Microsoft Copilot Studio license
- Power Platform environment
- Your custom application (any technology stack)
Step 1: Create Your Copilot Studio Agent
- Go to Copilot Studio
- Create a new Agent
- Create Topics with Event triggers (not phrase triggers)
- Define your AI prompts and logic
- Publish the agent
Step 2: Configure Event-Triggered Topics
For each use case, create a topic with:
- Trigger: “When an event is received”
- Event Name: Your custom event name (e.g., RefineContentEvent)
- Variable Extraction: Parse the event payload
- inputText = Text(System.Activity.Value.text)
- AI Processing: Add your generative AI prompts
- Response: Send a message with the result
Step 3: Get Your Token Endpoint
- In Copilot Studio, go to Settings → Channels
- Find the Token Endpoint URL for Direct Line
- Save this URL for your application configuration
Step 4: Implement in Your Application
Token Retrieval:
const response = await fetch(`${tokenEndpoint}?api-version=2022-03-01-preview`);
const { token, conversationId } = await response.json();
Start Conversation:
const conversation = await fetch(‘https://directline.botframework.com/v3/directline/conversations’, {
method: ‘POST’,
headers: { ‘Authorization’: `Bearer ${token}` }
});
Send Event:
await fetch(`${directLineUrl}/conversations/${conversationId}/activities`, {
method: ‘POST’,
headers: {
‘Authorization’: `Bearer ${token}`,
‘Content-Type’: ‘application/json’
},
body: JSON.stringify({
type: ‘event’,
name: ‘YourEventName’,
value: { /* your payload */ },
from: { id: ‘user-id’ }
})
});
Poll for Response:
const activities = await fetch(
`${directLineUrl}/conversations/${conversationId}/activities?watermark=${watermark}`,
{ headers: { ‘Authorization’: `Bearer ${token}` }}
);
const botMessage = activities.find(a => a.type === ‘message’ && a.from.id !== ‘user-id’);
Modernizing Legacy Applications with AI
Many organizations are sitting on a goldmine of legacy applications — systems built years ago that still power critical business processes. These applications often:
- Run on older technology stacks (.NET Framework, Classic ASP, Java, PHP, etc.)
- Have complex codebases that are risky to modify
- Lacks the budget or resources for complete rewrites
- Still deliver significant business value despite their age
The challenge? How do you add modern AI capabilities to these applications without a costly rebuild?
Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations
| Approach | Challenge |
| Full Rewrite | Expensive, time-consuming, high risk |
| Embed AI SDKs | Requires code changes, may not be compatible with legacy frameworks |
| Chatbot Widget | Feels disconnected from the app, poor user experience |
| Custom AI Backend | Requires AI expertise, infrastructure management, ongoing maintenance |
Why Direct Line API is Perfect for Legacy Apps
The Direct Line API + Copilot Studio pattern solves this elegantly:
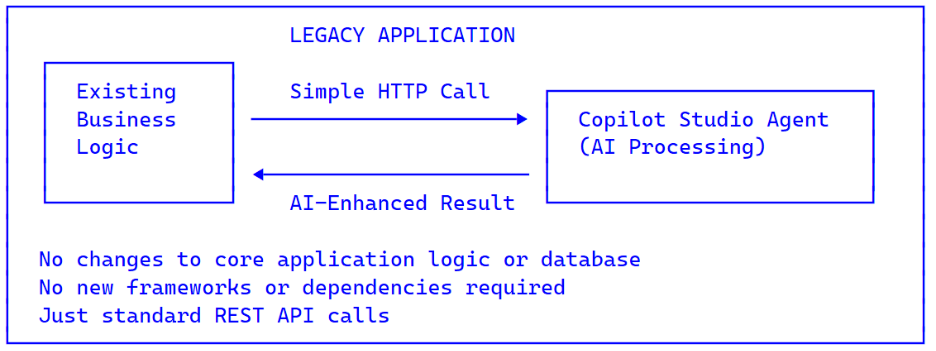
Why this works for legacy apps:
- REST API Based — Any application that can make HTTP calls can integrate (virtually all can).
- No SDK Required — No need to install AI libraries or update frameworks.
- Non-Invasive — Add AI features without touching core business logic.
- Incremental Adoption — Start with one feature, expand over time.
Centralized AI Logic — All AI prompts and logic managed in Copilot Studio, not in your legacy code.
Legacy Modernization Examples
| Legacy System | AI Enhancement | Business Value |
| Classic CRM (2010s) | Lead scoring, email drafting | Sales productivity boost |
| On-prem HR Portal | Policy Q&A, request processing | Reduced HR ticket volume |
| Legacy ERP | Document summarization, data extraction | Faster processing times |
| Old Ticketing System | Auto-categorization, resolution suggestions | Improved first-call resolution |
| Mainframe-connected Apps | Natural language queries, report generation | Self-service analytics |
Code Example: Adding AI to a Legacy .NET Application
Even a classic ASP.NET WebForms or MVC application can integrate:
// Simple HTTP call – works in .NET Framework 4.x
public async Task<string> RefineContentWithAI(string content, string instructions)
{
// Get token
var token = await GetCopilotStudioToken();
// Start conversation
var conversationId = await StartConversation(token);
// Send event to Copilot Studio Agent
var payload = new {
type = “event”,
name = “RefineContentEvent”,
value = new { text = content, instructions = instructions },
from = new { id = “legacy-app-user” }
};
await SendActivity(token, conversationId, payload);
// Poll for AI response
return await PollForResponse(token, conversationId);
}
The same pattern works for Java, PHP, Python, or any language with HTTP capabilities.
Best Practices
Design Principles
- Specific Events — Create focused events for specific actions rather than generic “ask AI” events.
- Structured Payloads — Define clear input schemas for each event type.
- Graceful Failures — Handle timeouts and errors with meaningful fallbacks.
- Caching — Cache tokens and reuse conversations where appropriate.
Security Considerations
- Backend Proxy — In production, route Direct Line calls through your backend to protect tokens.
- Input Validation — Validate payloads before sending to the agent.
- Output Sanitization — Sanitize AI responses before displaying to users.
- Rate Limiting — Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse.
Performance Tips
- Connection Reuse — Reuse conversations for multiple interactions when possible.
- Polling Optimization — Use appropriate polling intervals (2-3 seconds).
- Timeout Handling — Set reasonable timeouts for AI responses (30-60 seconds).
- Watermark Tracking — Always track watermarks to avoid processing duplicate messages.
Conclusion
The Direct Line API opens up exciting possibilities for integrating AI capabilities into any application without compromising on user experience. By leveraging Microsoft Copilot Studio Agents, organizations can:
- Embed intelligent automation into existing workflows
- Centralize AI logic for easier management and updates
- Connect to enterprise systems via the Power Platform ecosystem
- Scale effortlessly with Microsoft’s infrastructure
Whether you’re building document processing tools, customer support systems, or industry-specific applications, this pattern provides a flexible, powerful foundation for AI integration.
The key insight is that AI doesn’t have to mean chatbots. Sometimes the most effective AI integration is invisible — working behind the scenes to enhance your application’s capabilities while your users enjoy a familiar, streamlined experience.
Resources
Have questions or want to discuss implementation strategies? Reach out to the team at Netwoven Inc.























