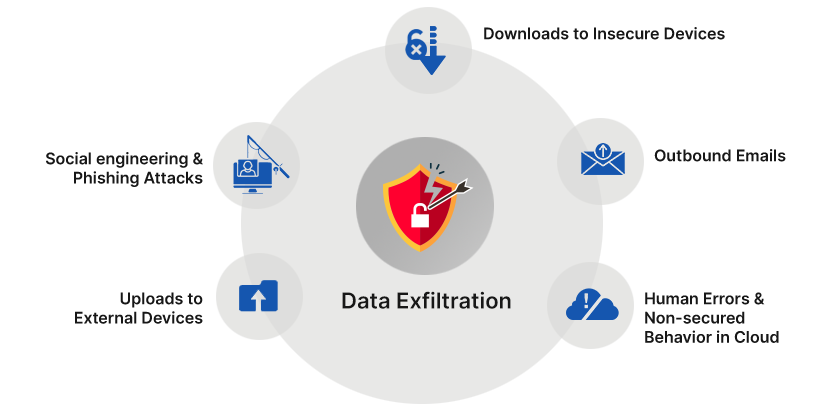
Data exfiltration commonly stands for theft or unauthorized removal or movement of data from a device. It typically involves cybercriminals stealing data from personal or corporate devices.
Technically, data exfiltration refers to extrusion, leakage, or theft of data that can pose serious financial or reputational problems for an organization and lead to misuse and abuse of sensitive information and eventually lawsuits.
Data exfiltration is often done either physically or digitally, in most cases, through emails, such as phishing. The target data can be employee information, customer database, intellectual property, payment card details, Personally Identifiable Information (PII), or other financial information.
How to detect data exfiltration
Detection of data exfiltration can be difficult. Cyberattack weapons often lurk in the system for months or years and it is realized when the damage is done. To detect the presence of bad actors, organizations must look into data exfiltration tools that discover malicious or unusual traffic automatically and in real time.
Here are seven data exfiltration techniques and how you can avoid them:
1. Detect and Stop Phishing Attacks
Perpetrators of phishing attack trace their route through human errors, bypassing insufficient security solutions. Some organizations use some less-effective and traditional schemes such as blocking domains, Security Email Gateways (SEGs), and Rule-Based solutions. These signature-based methods cannot protect against highly personalized, low-volume, targeted attacks that do not include any identifiable malicious content. Socially engineered attacks do not contain any traditional indicators of compromise. The best way to protect against email threats is to detect and stop fraudulent emails before they reach employee inboxes. Machine-intelligent email security solutions can learn from and understand the local context, communication relationships, and behavior patterns within an organization. They can identify any subtle deviations from typical behavior and stop targeted, socially engineered attacks that traditional email security systems fail to detect.
2. Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a set of business policies and technologies designed to ensure end-users cannot send sensitive or confidential data outside the organization. It scans all outbound emails, monitor them for pre-determined patterns that might indicate a person is transmitting sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers. Depending on the policy, if an email contains text that matches this format, the program automatically encrypts the data or blocks it from being sent.
3. Disable Unauthorized Channels and Protocols
It’s essential for an organization to keep track of employees who have access to which level of classified information, and revoke all such accesses to a partner or an employee after termination of the business relationship. Allowing someone to enjoy access to such data even for one day could lead to a security breach with severe productivity, reputational, or monetary consequences.
4. Implement Backup and Data Encryption Processes
In case of a security breach, it is vital to be prepared and ensure all data are backed up so they are available for quick restoration. Failure to back up data can lead to significant losses. Encryption policies, on the other hand, help keep the data safe while in transit. Cybercriminals cannot intercept or tamper with encrypted messages. Once the data is converted to ciphertext, it needs a unique key to be unlocked and decrypted.
5. Design and Implement Network Segmentation
By dividing a network into smaller segments, organizations can isolate critical data and restrict access to authorized personnel only. This reduces the attack surface and makes it more difficult for an attacker to move laterally within the network to exfiltrate data.
6. Firm up Endpoint Security
Unprotected endpoints, such as laptops, mobile devices, and IoT devices, can be compromised to gain access to sensitive data. Use endpoint protection solutions, enforce strong password policies, and regularly update and patch endpoint devices to minimize vulnerabilities.
7. Educate Employees
Human error poses one of the biggest threats of data exfiltration to any organization. Employees can make mistakes that attackers can leverage or employees could be compromised. A user could unsuspectingly download an infected malware file, transmit their credentials through a phishing campaign, or may as well be negligent in securing their personal computer or other devices. It is essential for an organization to regularly educate, train and upgrade its employees on the latest security measures to avoid human errors. Each employee should know how to spot and flag a suspicious email and escalate the matter to the security team to investigate and take necessary action without delay. All employees must be mindful of how to perform their security tasks effectively. Lastly, there must be clear understanding of compliance policies, laws and globally best practices among the employees.
Cyber criminals unleashed a wave of attacks in 2022 that were not just highly coordinated, but far more advanced than ever before. Simple endpoint attacks became complex, multi-stage, coordinated operations. Small businesses and big corporations were hit alike by ransomware attacks, while cryptomining attacks gave the cyber criminals an easy foothold into company networks. It was a year of massive data leaks, expensive ransomware pay-outs, and the opening up of a vast, new, complicated threat landscape for organizations world over.
Data is becoming more and more precious by the day. There are sensitive and classified information with every organization, big or small, across industries on its clients, rivals, employees, strategies, businesses and financials and any loss to such data wreaks havoc for the company. The worsening threat of data exfiltration puts this most important resource for a company at stake. The threat can be estimated by simple statistics: The data exfiltration services market is now expected to grow from $66.5 billion in 2020 to $145.1 billion by 2031 at an expected average annual growth rate of 23.7 per cent.
It’s time you save your data from falling into wrong hands.