Introduction:
One of the most common complaints we hear from employees when assessing existing corporate intranets is that “search sucks”. Often times this is a combination of using an outdated platform, having poor information architecture, and a lack of proper configuration of their search architecture. The Microsoft 365 platform provides a wide array of configuration options for searching contents throughout the entire tenant, alongside the internet and 3rd party applications, but understanding all these settings can be a daunting task, even for a trained administrator. In this blog we are going to take a deeper look into the available search configuration options and how to utilize them to give your employees a better experience when trying to find content. Let’s dive in!
SharePoint Search vs Microsoft Search
SharePoint has been around seemingly since the dawn of time and so has the ability to search its trove of wonders. Before Microsoft 365, configuring search for SharePoint was a key component for anyone involved with planning, implementing, and administering a corporate intranet. Nowadays, with SharePoint Online being the backend for Teams, Viva Engage, and OneDrive, the ability to effectively search its contents becomes even more paramount. However, SharePoint Search configuration has been heavily documented over the years, so we are going to focus solely on “Microsoft Search”, which is Microsoft’s way of allowing people to be able to search not only SharePoint but also the whole world wide web as well as the contents of other third-party applications to which the user has access to.
If you’ve already dabbled in SharePoint search configuration in the past, you may have noticed a new section in your Site Settings for Microsoft Search.
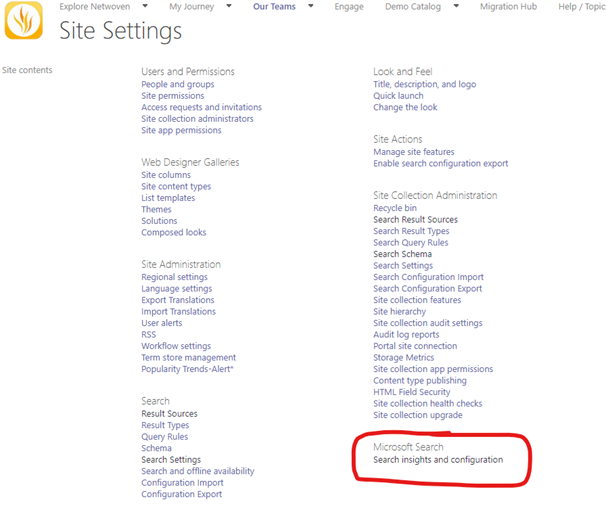
The main difference between SharePoint Search and Microsoft Search is simply the scope. A lot of the same functionality that exists in the site collection level search configurations is also available in the Microsoft Search configurations, but you can only use one or the other, and the settings that get used are based on the scope of the search that is available to the user on the page that they are currently searching from.
To put it simply, any SharePoint Online site that is configured to have a “site” or “hub” scope for the search box will use the site collection search settings, while sites configured to have a “tenant” scope will be using the Microsoft Search settings. The most commonly used configuration options (in SharePoint search terms) are result sources, result types, and query rules (search schema is too, but the same settings are used for both SharePoint and Microsoft search). In Microsoft search terms, result sources are called “Content Sources”, query rules are configured as “Answers” (more on this later), and result types are still called “Result Types”. Microsoft search is configured in the M365 Admin Portal whereas SharePoint search is configured within SharePoint, in the site settings menu.
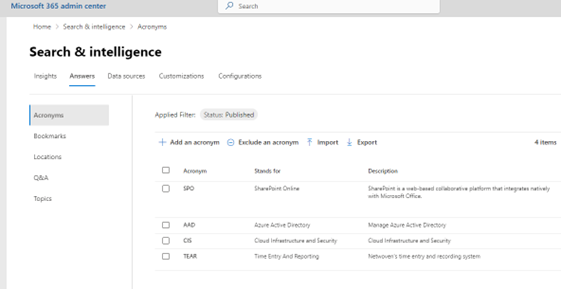
Lastly, Microsoft search results are also leveraged on Bing.com and new windows or tabs in Microsoft Edge.
As SharePoint search configuration has been documented heavily and, in much detail, we will focus the rest of this blog on Microsoft Search. The key thing to remember is that if you scope your site’s search box (through PowerShell) to “Hub” or “Site”, then the settings for SharePoint search will be used, whereas using the “Tenant” scope will use the settings for Microsoft search. You can change the scope settings for any site by running the following PowerShell and replacing “scope” with either Tenant, Hub, Site, or Default.
$SiteURL = “https://yourcompany.sharepoint.com/sites/SomeSite”
Connect-PnPOnline -Url $SiteURL -Interactive
Set-PnPSearchSettings -SearchScope scope
Free Download: Microsoft 365 Modern Intranet & Employee Experience Look Book
Configuring Microsoft Search
The configuration options for Microsoft Search can be found under the Search & Intelligence area within the Microsoft 365 Admin Center. You can access this by going to https://admin.microsoft.com and logging in with a Global Admin, Search Administrator, or Knowledge Administrator account, clicking on Settings in the left nav, then Search & Intelligence.
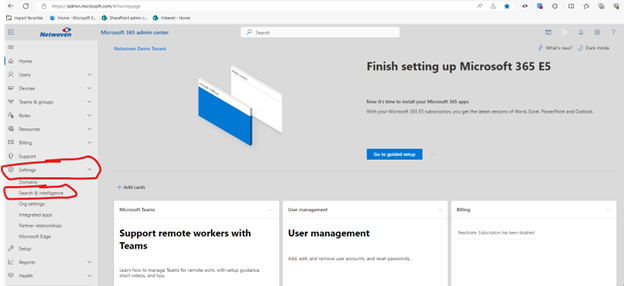
We’ll go through the configurations in order.

Microsoft 365 Modern Intranet & Employee Experience Look Book
In this look book, you’ll see examples of how Netwoven has created layouts and solutions for clients to enhance employee experiences with a modern intranet on Microsoft 365. Download now!
Get the Look BookInsights
The Insights tab gives you (somewhat) detailed analytics about all of the different search facets that we will be configuring for Microsoft Search. Make sure you’ve got the slider for “New usage analytics” turned on in order to view data with additional filters.
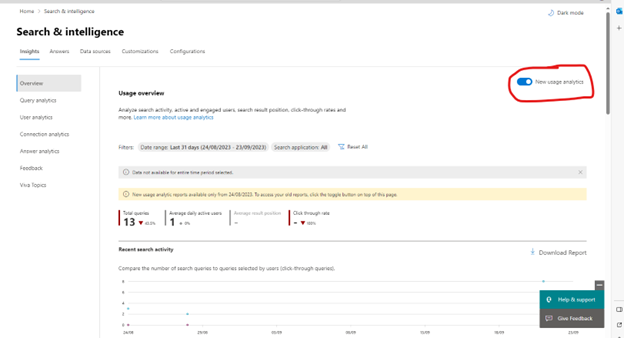
Our focus in this blog is to discuss configuration options, so we’ll save the analytics for another day. The descriptions are pretty self-explanatory, and it definitely makes sense to keep a constant eye on query and user analytics to find out exactly what your users are searching for and how often they are finding it.
Get to know Deep Dive into Microsoft Search Part-2
Get to know Deep Dive into Microsoft Search Part-3
Conclusion
We’ve just begun to scratch the surface so get your claws ready for the rest of this blog series. Microsoft Search is the new and super-powerful way to bring the whole world (well, the internet and everything work-related that your users have access to) right to your employees’ door (monitor). Search doesn’t have to suck, and Microsoft Search can make sure it doesn’t, but it needs some configuration. Tune in to part 2 of our Deep Dive where we will review everything you’ve ever wanted to know about Answers in Microsoft Search.