Introduction
Microsoft Fabric offers a cohesive Software as a Service (SaaS) solution, encompassing the essential functionalities for analytics across Power BI, Microsoft Azure Data Factory, and the upcoming iteration of Synapse. Fabric consolidates data warehousing, data engineering, data science, data integration, applied observability (through the Data Activator experience), real-time analytics, applied observability (through the Data Activator experience), and business intelligence within a unified architecture.
We try to give a clear and concise explanation to our customers on Microsoft Fabric internals so that this explanation gives customers a direction on how it differs from other data warehouses. How important role It play in enterprise digitalization.
Key Differentiators and Importance
Unified Experience
Unlike traditional siloed solutions, Fabric provides a seamless end-to-end experience for data management, analytics, and observability.
Efficiency
By consolidating services, Fabric streamlines workflows, reduces complexity, and accelerates time-to-insights.
Scalability
Fabric scales effortlessly to handle enterprise-scale data volumes and diverse workloads.
Strategic Impact
As organizations embrace digital transformation, Fabric becomes a strategic enabler for data-driven decision-making, innovation, and growth.
Microsoft Fabric isn’t just another data warehouse—it’s a holistic ecosystem that empowers enterprises to harness their data effectively and drive meaningful outcomes.
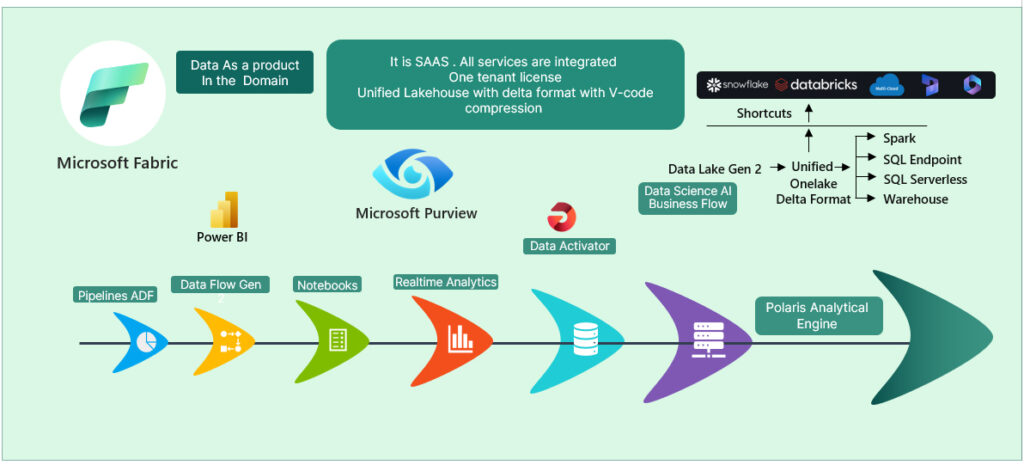
Let’s us deep dive into the fascinating world of Unified Data Management
1. Lakehouse Delta Lake Format with V-Order Compression and Versioning
- The concept of a lakehouse combines the best data lakes and data warehouses. It allows organizations to store vast amounts of raw data while also providing a warehouse’s structure and query capabilities.
- Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer that brings ACID transactions to Apache Spark and big data workloads. It ensures data consistency, reliability, and performance.
- V-Order compression is a technique that compresses data using variable-length codes, optimizing storage efficiency.
2. Bin Compaction for Improved Performance
- Bin compaction optimizes storage by grouping data into bins or segments. It reduces fragmentation and enhances query performance.
3. Virtual Warehouses and Serverless Pools
- Virtual warehouses are scalable, on-demand computing resources for running queries against data stored in cloud data warehouses.
- Serverless pools provide automatic scaling based on workload demand, allowing efficient resource utilization without manual provisioning.
4. Integrated Services
- A unified approach integrates various data services, such as data cataloging, lineage tracking, and governance, into a cohesive platform.
5. BI Reporting and Data Science in One Platform
- Having business intelligence (BI) reporting and data science tools within the same platform streamlines analytics workflows and promotes collaboration.
6. OneNote Book for Data Pipelines and Data Science
- OneNote provides a collaborative environment for documenting data pipelines, experiments, and insights.
7. Zero Table Cloning
- Eliminating table cloning reduces redundancy and simplifies data management.
8. Data Engineering Services
- These services encompass tasks related to data ingestion, transformation, and preparation.
9. Shortcuts with APIs for Custom Code
- Developers can create custom shortcuts using APIs, enhancing productivity and flexibility.
10. OneSecurity and Data Governance
- Ensuring data security and governance across the entire data lifecycle is critical for compliance and risk management.

Migrating to Fabric Warehouse
In this eBook, we will outline how Microsoft Fabric can significantly reduce the issues facing traditional data warehousing and provide a scalable platform for future growth.
Get the eBookMicrosoft Fabric Data Warehouse is an intriguing cloud-native data warehousing solution that harnesses the power of the Polaris distributed SQL query engine.
Let’s get into the details
1. Polaris Engine
- Stateless and Interactive: Polaris stands as a stateless, interactive relational query engine that drives the Fabric Data Warehouse. It’s designed to seamlessly unify data warehousing and big data workloads while segregating compute and state.
- Optimized for Analytics: Polaris is a distributed analytics system, meticulously optimized for analytical workloads. It operates as a columnar, in-memory engine, ensuring high efficiency and robust concurrency handling.
- Cell Abstraction: Polaris represents data using a unique “cell” abstraction with two dimensions:
- Distributions: Aligns data efficiently.
- Partitions: Enables data pruning.
- Cell Awareness: Polaris elevates the optimizer framework in SQL Server by introducing cell awareness. Each cell holds its own statistics, vital for the Query Optimizer (QO). This empowers the QO to implement diverse execution strategies and sophisticated estimation techniques, unlocking its full potential.
2. Fabric Data Warehouse Features
- Delta Lake Format: Fabric Warehouse persists data in Delta Lake format, ensuring reliability and transactional consistency.
- Separation of State and Compute: By decoupling state and compute, Fabric Warehouse achieves enhanced resource scalability and flexible scaling.
- Fine-Grained Orchestration: Task inputs are defined in terms of cells, allowing for fine-grained orchestration using state machines.
- Cloud-Native and Scalable: Polaris, being cloud-native, supports both big data and relational warehouse workloads. Its stateless architecture provides the flexibility and scalability needed for modern data platforms.
Webinar: Data Science for Business with Microsoft Fabric. Watch Now.
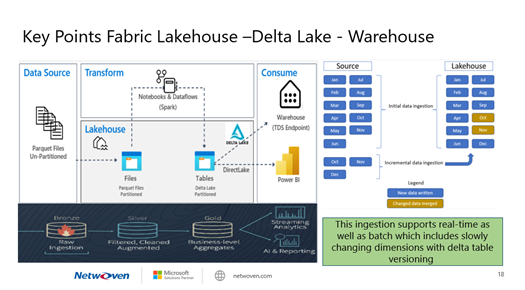
Let’s break down the Fabric components of the above architecture diagram
1. Delta Lake
- Delta Lake is an optimized storage layer that serves as the cornerstone for storing data and tables within the Databricks lakehouse architecture. It extends Parquet data files by adding a file-based transaction log for ACID transactions and scalable metadata handling.
- It ensures data reliability, consistency, and quality within your lakehouse architecture.
2. V-Order
- V-Order is a write-time optimization applied to the Parquet file format. It significantly enhances read performance under Microsoft Fabric compute engines (such as SQL, Spark, Power BI etc.).
- By sorting, distributing row groups, using dictionary encoding, and applying compression, V-Order reduces network, disk, and CPU resources during reads, resulting in cost efficiency and improved performance.
- It has a 15% impact on average write times but provides up to 50% more compression. Importantly, Delta Lake stays fully compliant with the open-source Parquet format, ensuring compatibility.
3. Unified Data Lakehouse
- You’re aiming for a unified architecture that combines the best of both data lakes and data warehouses.
- Here’s how you can structure it
- Bronze Zone: Raw, unprocessed data lands here.
- Silver Zone: Data is cleaned, transformed, and enriched.
- Gold Zone: Aggregated, curated data for business intelligence (BI) and machine learning (ML)/AI purposes.
- Data Warehouse: The gold zone serves as your data warehouse, providing a trusted source for BI queries.
- Fabric Copilot: Fabric Copilot ensures data quality and truth across all zones.
4. Integration
- Delta Lake tables, with features like Z-Order, are compatible with V-Order.
- You can control V-Order writes at the session level using Spark configurations.
- Remember that V-Order is applied at the Parquet file level, orthogonal to other Delta features like compaction, vacuum, and time travel
In summary, your architecture combines Delta Lake, V-Order, and a unified data lakehouse to achieve trusted data quality for ML/AI, BI, and analytics.
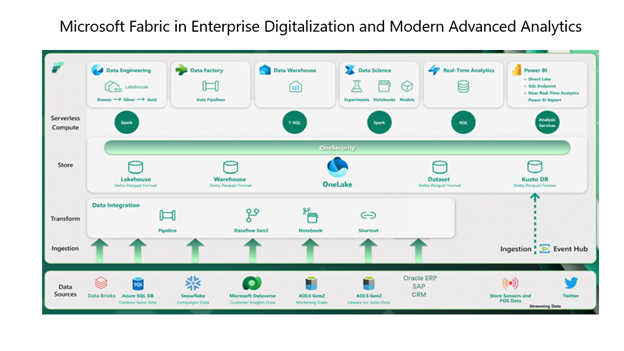
The Fabric, a unified SaaS experience, integrates Data Observability within its architecture.
Here are the key points
- Unified Platform: Fabric combines capabilities for analytics across Microsoft Azure Data Factory, Power BI, and the next-gen Synapse.
- Comprehensive Offerings: Fabric provides Data Governance, Data Security, Data Integration, Data Engineering, Data Warehousing, Data Science, Real-time Analytics, Applied Observability (via the Data Activator), and Business Intelligence.
The Data Activator experience within the Fabric ecosystem is a novel module designed for real-time data detection and monitoring.
Let’s explore its key features
1. Real-Time Data Detection
- The Data Activator continuously scans incoming data streams, identifying patterns, anomalies, and events in real time.
- It leverages machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques to detect changes, spikes, or deviations from expected behavior.
- Whether it’s sudden spikes in website traffic, unexpected sensor readings, or unusual transaction patterns, the Data Activator raises alerts promptly.
2. Monitoring and Alerting
- Once detected, the Data Activator triggers alerts or notifications to relevant stakeholders.
- These alerts can be customized based on severity levels, thresholds, and specific conditions.
- Monitoring dashboards provide real-time visibility into data health, allowing data engineers and analysts to take immediate action.
3. Adaptive Learning
- The Data Activator learns from historical data and adapts its detection algorithms over time.
- As new data arrives, it refines its models, ensuring accurate and relevant alerts.
- Adaptive learning helps reduce false positives and enhances the system’s responsiveness.
4. Integration with Fabric Components
- The Data Activator seamlessly integrates with other Fabric components, such as data pipelines, data lakes, and analytics workflows.
- It complements existing observability features, enhancing the overall data management experience.
- By providing real-time insights, it empowers organizations to proactively address data quality, compliance, and operational challenges.
Conclusion
A unified data management approach combines data quality, observability, cataloging, governance, and lineage. It centralizes and automates data workflows, enabling organizations to harness the full potential of their data and analytics investments, and plays a key role in enterprise digitalization with AI
Microsoft Fabric Data Warehouse, powered by the Polaris engine, seamlessly bridges the gap between data warehousing and big data, all while embracing cloud-native principles.
the Data Activator experience is a crucial part of Fabric’s commitment to data observability, ensuring that data anomalies and issues are swiftly detected and addressed.