Introduction:
Microsoft Fabric, unveiled by Microsoft, stands as a unified Software as a Service (SaaS) platform intricately linked with existing Microsoft analytical tools such as Power BI, Azure Data Explorer, Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Data Factory. It delivers numerous benefits across seamless data discovery, streamlined integration time and data exchange.
Fabric’s data and operations find a home in OneLake, a unified, singular, logical data lake catering to the entire enterprise, embracing the concept of “data as a product” to support Data Mesh architecture. OneLake serves as a multi-cloud data lake, enabling enterprises to virtualize data lake storage across AWS S3, ADLS Gen2, and Google Storage, seamlessly integrating with Oracle OFS, SAP and other CRMs. Existing data lakes can be seamlessly incorporated within Fabric.
Within the Fabric ecosystem, all data is meticulously preserved in delta lake format, including warehouse data. Traditional relational storage is phased out, eliminating the need for maintaining separate data sets for data warehousing, data lakes, real-time analytics and business intelligence. Instead, all workloads can draw directly from a unified data repository within OneLake.
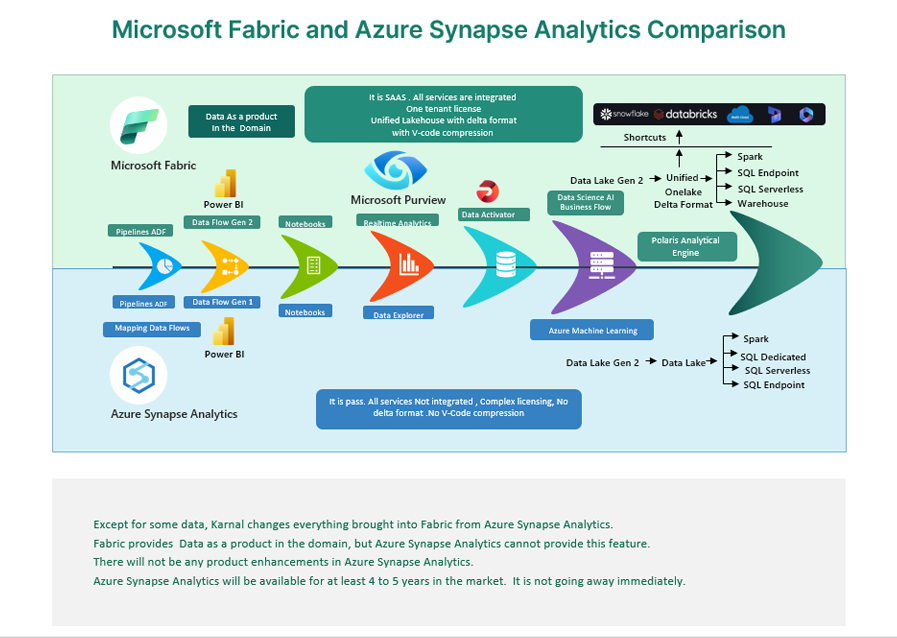
Microsoft has integrated Fabric Copilot into the Fabric environment, enhancing functionalities across dataflows, data engineering, and Power BI. Fabric consolidates nearly all Synapse functionalities, offering enhanced performance and integrated services within a single platform, promising a better return on investment as depicted in the architecture mapping image below.
Azure Synapse vs Fabric

Unlocking the Potential of Microsoft Fabric in Modern Advanced Analytics
In this comprehensive Ebook, we invite you to embark on a transformative journey, delving into the cutting-edge capabilities of Microsoft Fabric and OneLake.
Get the eBookSynapse vs Fabric: How do they differ from one another?
- Fabric operates as a Software as a Service (SaaS), offering less control and a fully managed service, while Synapse functions as a Platform as a Service (PaaS), providing more control and a higher level of responsibility.
- The Fabric warehouse operates on the Polaris engine, which supersedes the SQL distributed engine and also drives the Serverless SQL pool in Synapse. This massive parallel processing (MPP) engine automatically scales to accommodate various data workloads.
- Dataflows Gen2 (Power Query) can serve as an alternative to Mapping Data Flows. Synapse Mapping Data Flows offer a graphical user interface for “no code / low code” data transformation within Synapse, a feature not supported in Fabric.
- The use of OPENROWSET() is not supported. However, querying data from the lake(house) in Fabric is still possible using T-SQL with a SQL endpoint. It requires modifying all queries that employ OPENROWSET syntax.
- While the Synapse Link feature is absent in Fabric, it is substituted with Mirroring. Fabric introduces the Data Activator module, designed for real-time data detection and monitoring. It can send notifications and execute actions upon detecting specific data patterns.
- The Spark engine in Fabric spins up significantly faster than the Synapse engine in 2 to 4 seconds against 2 minutes. It is a native integrated part of Fabric.
Don’t miss this opportunity to expand your knowledge and harness the full potential of Microsoft Fabric. Watch our webinar on-demand!
Conclusion
Fabric enables next-generation data and analytics capabilities such as Lakehouse, Data Mesh, and Data Virtualization. However, keep in mind that everything announced is still in preview. Organizations that utilize Azure Synapse Analytics should consider Microsoft Fabric and how it fits with their technological roadmap. Certain Synapse features (most notably, Mapping Dataflows and OPENROWSET() syntax in SQL queries over files in a data lake) are not supported in Fabric. As such, for Synapse vs Azure Fabric there exists no “lift-and-shift” approach.